For example, Companies A and B both pay an annual dividend of $2 dividend per share. Company A’s stock is priced at $50 per share, however, while Company B’s stock is priced at $100 per share. Company A’s dividend yield is 4% while Company B’s yield is only 2%, meaning Company A could be a better bet for an income investor. Some investors, such as retirees, are heavily reliant on dividends for their income. For other investors, dividend yield may be less significant, such as for younger investors who are more interested in growth companies that can retain their earnings and use them to finance their growth. For example, qualified dividends are taxed in the United States at a lower rate than ordinary income, with rates ranging from 0% to 20% depending on the investor’s tax bracket.
Other Indicators of Company Health

This preferential treatment is designed to encourage investment in dividend-paying stocks. Non-qualified dividends, however, are taxed at the individual’s regular income tax rate, which can be substantially higher. A company’s ability to consistently pay and increase dividends is often a strong indicator of its financial health and stability. Companies that generate sufficient profits and cash flow are more likely to distribute dividends to their shareholders.
- The dividend rate is the annual amount of the company’s dividend per share.
- Dividend yield, on the other hand, refers to a stock’s annual dividend payments divided by the stock’s current price, and expressed as a percentage.
- Investors who target having a minimum cash inflow from their investment portfolio can ensure this by making investments in stocks that regularly pay relatively high and stable dividend yields.
- But it’s important to have a good understanding of dividends, dividend yields, and other related concepts before going too far into the weeds.
Dividend Payout Ratio (DPR)
If a company’s dividend yield is substantially different from its industry peers, or from the company’s own typical levels, that can be an indicator of whether the company is trading at the right valuation. Suppose we have two companies – Company A and Company B – each trading at $100.00 with an annual dividend per share (DPS) of $2.00 in Year 1. Since the yield is denoted as a percentage, shareholders can easily assess their expected returns per dollar invested.
Understanding Dividends
It is also represented as a company’s total annual dividend payments divided by its market capitalization, assuming the number of shares is constant. Historically, the Dow Jones dividend yield has fluctuated between 3.2% (during market highs, for example in 1929) and around 8.0% (during typical market lows). The highest ever Dow Jones dividend yield occurred in 1932 when it yielded over 15%, which was years after the famous stock market collapse of 1929, when it yielded only 3.1%. Calculating the dividend yield of an investment is useful for investors who want to compare companies and the dividends they pay. For investors looking for investments to help supplement their cash flow, or even to possibly live off dividend income, a higher dividend yield on a stock would be more attractive than a lower one. Up to a certain point, companies with increasing dividend yields tend to be healthier investments than ones with decreasing yields.
Focusing exclusively on dividend yield can also cause investors to miss out on better opportunities. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. Here’s what you should know about dividend yields, including how to calculate them. The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us.
Smaller companies with aggressive growth targets are less likely to offer dividends, but rather spend their excess capital on expansion. Thus, investors focused solely on dividend income could miss out on some faster-growing opportunities. • From a valuation perspective, dividend yield can be a useful point of comparison.
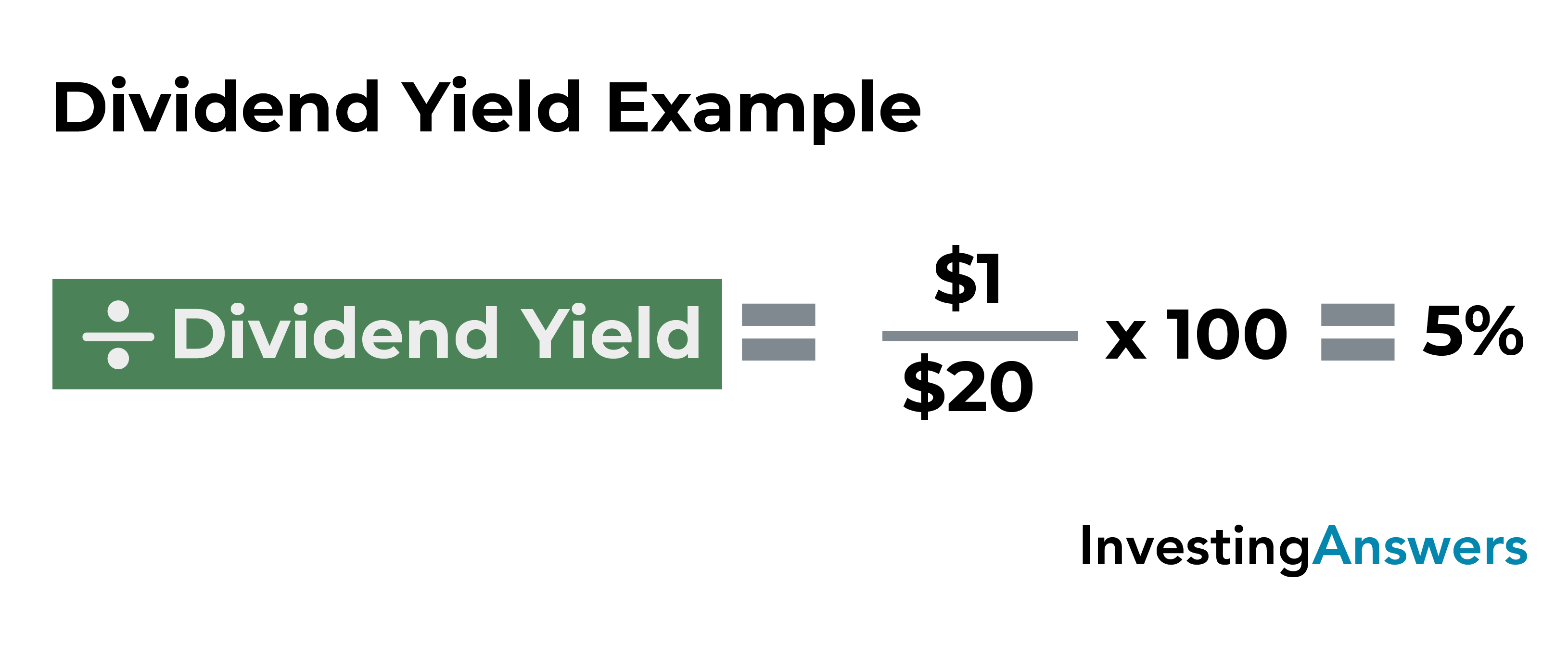
But if the increase stems from a declining share price, that would be a concerning sign. The dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share (DPS) by the current market share price and expressed as a percentage. The dividend payout ratio is another way of looking at dividends, and in certain circumstances it may shed some light on whether a big dividend is sustainable. This is another simple calculation that shows dividend payouts as a percentage of a company’s total profits. To arrive at this number, divide the total amount of dividends paid in a period by net income from the same period.
But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you. Any estimates based on past performance do not a guarantee future performance, and prior to making any investment you should discuss your specific investment needs or seek advice from a qualified turbotax super bowl commercial tv ad 2021 and #taxfacts professional. When dividends are paid, the cash is automatically deposited into your brokerage account. You can refer to financial websites such as this one to see the dividend yield, which is listed along with other key data points such as P/E Ratio and Earnings Per Share (EPS) when you look up a stock. For example, in the image below you can see the dividend yield listed for Duke Energy.
Regular dividend payments can also boost shareholder confidence, signaling that management is confident in the company’s future prospects and earnings potential. This consistent payout demonstrates that the company generates sufficient profits to share with its shareholders. Not only is this another signal of good financial health, it can be an indicator that management has a plan for the future and believes it does not need cashflow for future success. In some cases, the dividend yield may not provide that much information about what kind of dividend the company pays. For example, the average dividend yield in the market can be very high amongst real estate investment trusts (REITs).
Stock dividends are not taxed as they are earned if they are in a retirement account. Typically, it is large, established companies with steady profits which pay dividends. Companies paying dividends are often in the financial, energy, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, telecommunication, consumer goods, information technology, real estate, and utility sectors.
Dividends can be awarded as additional stock, cash, or other forms of consideration. Investors should exercise caution when evaluating a company that looks distressed and has a higher-than-average dividend yield. Because the stock’s price is the denominator of the dividend yield equation, a strong downtrend can increase the quotient of the calculation dramatically. The lesson here is that focusing too closely on yield can cause you to invest in struggling companies and overlook investments that could do more to boost your total wealth.